| Carangidae (Jacks and pompanos), subfamily: Naucratinae |
| 160 cm FL (male/unsexed); max.weight: 60 kg |
|
reef-associated; depth range 5 - 245 m |
| Circumglobal. Indo-West Pacific: Kenya south to South Africa (Ref. 3287) and east to Mariana and Wake islands in Micronesia, north to the Ryukyu Islands, south to New Caledonia and the Kermadec Islands (Ref. 8879). Absent from the Red Sea and French Polynesia. Likely at Seychelles (Ref. 1623). Eastern Pacific: USA to Peru, including Galapagos Islands (Ref. 2850). Western Atlantic: Cape Cod, USA to northern Argentina (Ref. 9626). Distribution in the eastern Atlantic is not well established. Recently recorded from Lampedusa Island in the Mediterranean (Ref. 47878). |
|
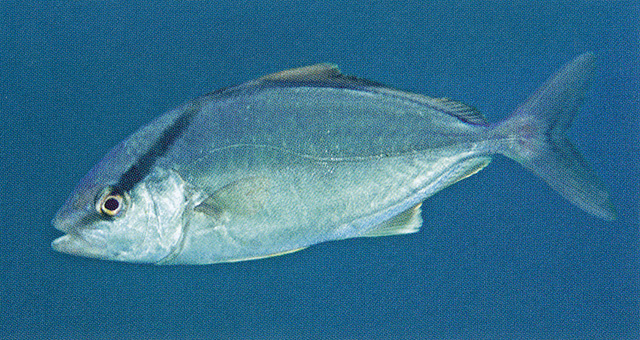
Dorsal spines (total): 8-8; Dorsal soft rays (total): 27-33; Anal spines: 3-3; Anal soft rays: 18-22. Description: Color highly variable when fresh. Dorsal brown or silvery blue-green to olivaceous, ventral paler or silvery with brassy or lavender reflections; vertical bar on nape dark; oblique stripe (may be absent), midlateral, yellow, amber or dark yellow brown, from eye or from mouth through eye to dorsal back profile near anterior dorsal fins; fins dark or yellowish grey except pelvic fins, white ventrally (Ref. 3197, 55763, 90102). Body elongated, moderately deep, slightly compressed; profile more convex on dorsal than ventral. Upper jaw posterior very broad, extends to level of middle of pupil. Gill rakers usually 6-9 + 18-20 = 24 -29 total gill rakers but 22 to 26 (excluding rudiments) in fish larger than 20 cm FL (Ref. 90102); first gill arch lower branch with 15 to 18 gill rakers in individuals greater than 20 cm SL (Ref. 55763). Supra-maxillary very wide. LL forms dermal keel on the caudal peduncle. Second dorsal fin anterior lobe deep; caudal peduncle with dorsal and ventral fossae (Ref. 55763). Dorsal fin lobe longer than pectoral fins 1.3 to 1.6 times and 18 to 22 % FL (Ref. 90102). |
| Adults are benthopelagic in outer reef slopes and offshore banks to 160 m or more. They form small groups (Ref. 9283, 26235, 58302). Young often seen around floating objects (Ref. 4887, 48635). They feed mainly on fishes, but also on invertebrates. Eggs are pelagic (Ref. 4233). Marketed fresh and salted or dried (Ref. 9283). May cause ciguatera poisoning, particularly in coral reef areas (Ref. 5217). Uncommon on East Indian reefs but occasionally found in cool upwelling areas of Lesser Sunda Islands of Indonesia (Ref. 90102). |
|
(Ref. 96402)
|
| reports of ciguatera poisoning |
|
Source and more info: www.fishbase.org. For personal, classroom, and other internal use only. Not for publication.
Page created by Jen, 05.08.02,
php script by kbanasihan 06/09/2010 ,
last modified by
dsantos, 20/08/10