Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) >
Perciformes (Perch-likes) >
Lutjanidae (Snappers) > Lutjaninae
Etymology: Lutjanus: Malay, ikan lutjan, name of a fish.
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
Marine; reef-associated; depth range 1 - 60 m (Ref. 9710). Tropical, preferred ?; 31°N - 27°S, 31°E - 136°W (Ref. 55)
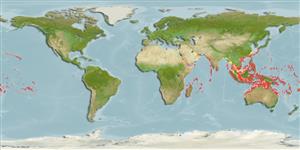
Indo-Pacific: East Africa to the Marquesas and Line islands, north to the Ryukyu Islands, south to Australia.
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 60.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 55); common length : 50.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 55)
Dorsal
spines
(total): 10;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 13-14;
Anal
spines: 3;
Anal
soft rays: 8 - 9. Adults grey or yellowish grey to brown with yellow fins. At night it is brown to red in color. With or without black side spot that can be turned on or off at will (Ref. 48635). Dorsal profile of head gently to moderately sloped. Preorbital width about equal to eye diameter. Preopercular notch and knob poorly developed. Scale rows on back rising obliquely above lateral line. Generally silvery white with yellow fins, and usually a black spot below the middle of the dorsal fin that is intersected by the lateral line (Ref. 469). Body depth 2.6-3.0 in SL (Ref. 90102).
Adults inhabit coral reef areas, usually close to shelter in the form of caves, large coral formations and wreckage. Usually solitary; occasionally occurring in small groups. They feed mainly on fishes and benthic crustaceans, primarily crabs (Ref. 37816) at night. Flesh is sometimes ciguatoxic, and commonly so in Tuvalu (Ref. 9513).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Allen, G.R., 1985. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 6. Snappers of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of lutjanid species known to date. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(6):208 p. Rome: FAO. (Ref. 55)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
CITES (Ref. 94142)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Reports of ciguatera poisoning (Ref. 4690)
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; aquaculture: commercial
More information
ReferencesAquacultureAquaculture profileStrainsGeneticsAllele frequenciesHeritabilityDiseasesProcessingMass conversion
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources