Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) >
Perciformes (Perch-likes) >
Serranidae (Sea basses: groupers and fairy basslets) > Epinephelinae
Etymology: Epinephelus: Greek, epinephelos = cloudy (Ref. 45335).
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
Marine; reef-associated; oceanodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 1 - 46 m (Ref. 9710). Tropical, preferred 27°C (Ref. 107945); 30°N - 34°S, 27°E - 134°W (Ref. 5222)
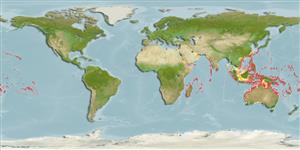
Indo-Pacific: Red Sea and east coast of Africa to French Polynesia. In the western Pacific it ranges from southern Japan to southern Queensland and Lord Howe Island. Often confused with Epinephelus fuscoguttatus.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ?, range 58 - ? cm
Max length : 90.0 cm SL male/unsexed; (Ref. 4319); common length : 90.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5450)
Dorsal
spines
(total): 11;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 14-15;
Anal
spines: 3;
Anal
soft rays: 8. Distinguished by the following characteristics: pale brown color; head, body and fins covered by numerous small dark brown spots; whitish upper half of body with large irregular dark blotches and dark saddle on upper tail base; body scales ctenoid in broad zone on side from beneath pectoral fin to caudal peduncle, cycloid elsewhere; body with auxiliary scales; greatest depth of body 2.7-3.1 in SL; rounded caudal fin; short pelvic fins, 1.9-2.4 in head length (Ref. 90102); head length 2.3-2.5 times in SL; flat interorbital area, evenly convex dorsal head profile; rounded preopercle, serrae at angle slightly enlarged; very convex upper edge of operculum; posterior nostril diameter about twice diameter of anterior nostrils; maxilla reaches to or beyond vertical at rear edge of eye; 2-3 rows of teeth on midlateral part of lower jaw; front of jaws with inconspicuous fixed canines (Ref. 89707).
Usually found in coral-rich areas of lagoon and outer reefs; in caves and large crevices to swim through (Ref. 48635). Most abundant around islands, particularly atolls. Usually in small schools. Feeds mainly on crustaceans (portunid crabs) and fishes, sometimes on cephalopods and gastropods. In the Hong Kong live fish markets (Ref. 27253). Frequently ciguatoxic in the Marshall Is. (Ref. 37816). Solitary (Ref 90102).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Heemstra, P.C. and J.E. Randall, 1993. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 16. Groupers of the world (family Serranidae, subfamily Epinephelinae). An annotated and illustrated catalogue of the grouper, rockcod, hind, coral grouper and lyretail species known to date. Rome: FAO. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(16):382 p. (Ref. 5222)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
CITES (Ref. 94142)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Reports of ciguatera poisoning (Ref. 1602)
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; aquaculture: experimental
More information
ReferencesAquacultureAquaculture profileStrainsGeneticsAllele frequenciesHeritabilityDiseasesProcessingMass conversion
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources