Elasmobranchii (sharks and rays) >
Rhinopristiformes (Shovelnose rays) >
Rhinobatidae (Guitarfishes) > Rhinobatinae
Etymology: Rhinobatos: Greek, rhinos = nose + Greek, batis, -idos = a ray (Raja sp.) (Ref. 45335).
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
Marine; brackish; demersal; depth range 0 - 100 m (Ref. 12951). Subtropical, preferred ?; 44°N - 17°S, 19°W - 36°E
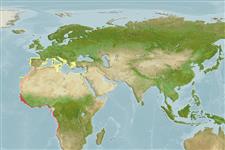
Eastern Atlantic: southern Bay of Biscay to Angola, including Mediterranean Sea.
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 147 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 36897); common length : 80.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 3261)
Dorsal
spines
(total): 0;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 0. Rostral ridges widely separated over their entire length; anterior nasal lobe reaching to level of inner corner of nostril, posterior nasal flap wide; spiracle with two moderately developed folds, the outer one more prominent; thorns relatively small, present around inner margin of orbits, between spiracles, on shoulders, and along midline of disc and tail; Upper surface khaki-brown, underside white (Ref. 6675).
Inhabits sandy and muddy bottoms, from the intertidal zone to about 100 m. Sometimes near rocky reefs (Ref. 12951). Slow swimming over bottom or partially buried. Feeds on benthic invertebrates and fishes. Ovoviviparous, one or two litters per year with 4-10 embryos.
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Exhibit ovoviparity (aplacental viviparity), with embryos feeding initially on yolk, then receiving additional nourishment from the mother by indirect absorption of uterine fluid enriched with mucus, fat or protein through specialised structures (Ref. 50449). One or two litters per year, of 4-10 embryos (Ref. 6675)
Schneider, W., 1990. FAO species identification sheets for fishery purposes. Field guide to the commercial marine resources of the Gulf of Guinea. Prepared and published with the support of the FAO Regional Office for Africa. Rome: FAO. 268 p. (Ref. 2683)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
CITES (Ref. 94142)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial
More information
ReferencesAquacultureAquaculture profileStrainsGeneticsAllele frequenciesHeritabilityDiseasesProcessingMass conversion
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources