Classification / Names
Common names from other countries
Main reference
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 180 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 40637); common length : 12.2 cm SL male/unsexed; (Ref. 35840); max. published weight: 35.0 kg (Ref. 56557); max. reported age: 13 years (Ref. 55930)
Length at first maturity
Lm 91.5, range 100 - ? cm
Environment
Freshwater; demersal; pH range: 7.5 - 8.5; potamodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 5 - 30 m (Ref. 6898)
Climate / Range
Subtropical; ? - 40°C (Ref. 55930), preferred ?; 53°N - 15°N, 100°E - 140°E (Ref. 55930)
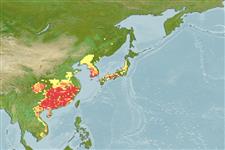
Distribution
Asia: Amur river basin to southern China (Ref. 55930). Reported from Vietnam (Ref. 44416). Persists only in Europe by stocking or accidental releases; native stocks in Russia have declined sharply (Ref. 59043). Several countries reported adverse ecological impact after introduction.
Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Short description
Dorsal
spines
(total): 0;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 7-9;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 8 - 10. Anatomy of the pharyngeal apparatus is the main distinguishing characteristic; throat teeth typically form a single row of 4-5 large molariform teeth on each of the two arches, with formula typically 1,4 - 4,1.
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Potential pest (Ref. 74657)
Human uses
Fisheries: highly commercial; aquaculture: commercial
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index
PD50 = 1.0000 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
3.2 ±0.44 se; Based on food items.
Resilience
Low, minimum population doubling time 4.5 - 14 years (K=0.08-0.09; tm=3-9; tmax >13; Fec=1,000,000)
Vulnerability
Very high vulnerability (80 of 100)
Price category