Classification / Names
Common names from other countries
Main reference
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 240 cm FL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5765); common length : 120 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5450); max. published weight: 70.0 kg (Ref. 5765)
Length at first maturity
Lm 85.0, range 55 - 82 cm
Environment
Marine; pelagic-neritic; oceanodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 10 - 70 m (Ref. 12260)
Climate / Range
Tropical, preferred 27°C (Ref. 107945); 39°N - 41°S, 7°W - 180°E (Ref. 54880)
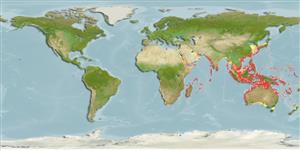
Distribution
Indo-West Pacific: Red Sea and South Africa to Southeast Asia, north to China and Japan and south to southeast Australia, and to Fiji (Ref. 6390). Immigrant to the eastern Mediterranean Sea by way of the Suez Canal. Southeast Atlantic: St. Helena.
Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Short description
Dorsal
spines
(total): 15 - 18;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 15-20;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 16 - 21;
Vertebrae: 42 - 46. Interpelvic process small and bifid. Swim bladder absent. Lateral line abruptly bent downward below end of second dorsal fin. Intestine with 2 folds and 3 limbs. Vertical bars on trunk sometimes break up into spots ventrally which number 40-50 in adults, and less than 20 in juveniles. Juveniles with large oval dark spots on body; middle third of first dorsal fin white, rest of fin black (Ref. 11228).
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Reports of ciguatera poisoning (Ref. 168)
Human uses
Fisheries: highly commercial; gamefish: yes
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index
PD50 = 0.5000 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
4.5 ±0.4 se; Based on diet studies.
Resilience
Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (K=0.12-0.21; tm=2-3; tmax=14; Fec=590,000)
Vulnerability
Moderate vulnerability (41 of 100)
Price category