Classification / Names
Common names from other countries
Main reference
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 750 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 58784); common length : 500 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 2683); max. published weight: 807.4 kg (Ref. 4699); max. reported age: 50 years (Ref. 4827)
Length at first maturity
Lm ?, range 210 - 350 cm
Environment
Marine; brackish; benthopelagic; oceanodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 0 - 800 m (Ref. 96339), usually 0 - 140 m (Ref. 26938)
Climate / Range
Subtropical, preferred 26°C (Ref. 107945); 62°N - 42°S, 180°W - 180°E
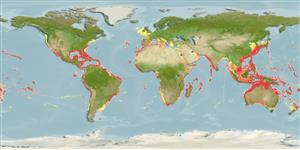
Distribution
Circumglobal in tropical and temperate seas. Western Atlantic: Massachusetts, USA to Uruguay, including Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean. Eastern Atlantic: Iceland to Angola. Indo-Pacific: Persian Gulf (Ref. 68964), Red Sea and East Africa to Hawaii and Tahiti, north to southern Japan, south to New Zealand. Eastern Pacific: southern California, USA to Peru, including the Revillagigedo, Cocos, and Galapagos islands. Highly migratory species, Annex I of the 1982 Convention on the Law of the Sea (Ref. 26139).
Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Short description
Dorsal
spines
(total): 0;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 0;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 0. A huge, vertical tiger-striped shark with a broad, bluntly rounded snout, long upper labial furrows, and a big mouth with large, saw-edged, cockscomb-shaped teeth; spiracles present; caudal keels low (Ref. 5578). Grey above with vertical dark grey to black bars and spots which appear faded in adults, white below (Ref. 5578).
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; gamefish: yes
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index
PD50 = 1.0000 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
4.5 ±0.0 se; Based on diet studies.
Resilience
Low, minimum population doubling time 4.5 - 14 years (tm=4-11; tmax=50; Fec = 10)
Vulnerability
High vulnerability (64 of 100)
Price category