Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) >
Scorpaeniformes (Scorpionfishes and flatheads) >
Platycephalidae (Flatheads)
Etymology: Platycephalus: Greek, platys = flat + Greek, kephale = head (Ref. 45335).
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
Marine; brackish; reef-associated; oceanodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 20 - 200 m (Ref. 36128). Subtropical, preferred 27°C (Ref. 107945); 32°N - 35°S, 18°E - 157°E
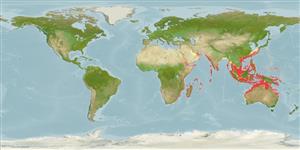
Indo-West Pacific: Red Sea and East Africa to the Philippines, north to southern Japan and Korea, south to northern Australia. Introduced into the eastern Mediterranean Sea.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 40.0 range ? - ? cm
Max length : 100.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 7050); common length : 60.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 3476); max. published weight: 3.5 kg (Ref. 40637)
Dorsal
spines
(total): 9 - 10;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 13;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 13. Brownish or grayish above, whitish below; caudal fin 2-3 horizontal black stripes (Ref. 4315). Head strongly depressed. Preopercular spines 2, lower usually longest. Vomerine teeth in a single transverse band. Dorsal fin I,VII,I, I,I,VII,I or I,VIII, 13. Anteriormost lateral line scale usually with a small spine or ridge. Diagonal scale rows slanting backward above lateral line 83-107. Iris lappet a single elongated lobe. Identified by the distinctive color pattern on the caudal fin: centrally yellow and black stripes on upper and lower margins (Ref. 48635).
Found on sandy and muddy bottoms of coastal waters (Ref. 5213, 48635). Frequently in estuaries, juveniles have been taken in freshwater. Taken by handlining and seining in shallow waters and by trawling at depths to 30 m, usually less (Ref. 9790). A good food fish (Ref. 4315) that is marketed fresh (Ref. 5284). Commercially cultured in Japan. Used in Chinese medicine (Ref. 12166).
Also Ref. 103751.
Bauchot, M.-L., 1987. Poissons osseux. p. 891-1421. In W. Fischer, M.L. Bauchot and M. Schneider (eds.) Fiches FAO d'identification pour les besoins de la pêche. (rev. 1). Méditerranée et mer Noire. Zone de pêche 37. Vol. II. Commission des Communautés Européennes and FAO, Rome. (Ref. 3397)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
CITES (Ref. 94142)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; aquaculture: commercial; gamefish: yes
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources