Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) >
Syngnathiformes (Pipefishes and seahorses) >
Syngnathidae (Pipefishes and seahorses) > Hippocampinae
Etymology: Hippocampus: Greek, ippos = horse + Greek,kampe = curvature (Ref. 45335).
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
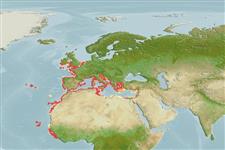
Marine; demersal; non-migratory; depth range ? - 60 m (Ref. 52034). Subtropical, preferred ?; 52°N - 2°N, 32°W - 42°E
Eastern Atlantic: British Isles and Wadden Sea southward to the Gulf of Guinea, the Azores (Ref. 89254), Canary Islands (89255) and along the African coast to Guinea. Also in the Mediterranean (89253).
International trade is monitored through a licensing system (CITES II, since 5.15.04) and a minimum size of 10 cm applies. Listed in Appendix II (Mediterranean) of the Bern Convention (2002) and in Appendix II (as Hippocampus spp.) at CITES (2009).
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 7.7 range ? - ? cm
Max length : 15.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 6733)
Short description
Morphology | Morphometrics
Dorsal
spines
(total): 0;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 16-19. Description (based on 35 specimens): Adult height: 7.0-13.0cm. Rings: 11 + 37 (35-38). Snout length: 3.0 (2.8-3.4) in head length. Dorsal fin rays: 17 (16-19) covering 2+1 rings. Pectoral fin rays: 14 (13-15). Coronet: narrow, ridge-like and joined smoothly to nape of neck, or wedge-shaped (front narrow, back high and broad); some specimens with very large angular coronet (especially specimens from West Africa). Spines: low, very low in adults. Other distinctive characters: very short snout (usually less than 1/3 head length) that is slightly upward-bent; prominent eye spine. Color pattern: mottled brown to yellow, to maroon and rust (Refs. 52034, 89230); also orange, purple or black; sometimes with tiny white dots, but these do not coalesce into thick horizontal wavy lines as in H. guttulatus.
Inhabits dense, complex habitats as well as patchy, relatively open and sparse habitats of coastal areas. Found on soft bottoms amongst rocks and algae (Ref. 6733), on sparsely vegetated areas, and in coastal lagoons with strong oceanic influences (Refs. 52034, 89230). Mimics the green or yellow coloration of plants allowing it to hide among the vegetation. This ability likely plays a role in seahorse feeding strategy and in predator avoidance (Ref. 52034). Makes limited daily movements within very restricted home ranges (0.7-18.1 m2) (Refs. 52034, 89256). May over-winter in deeper water. (Ref. 53712). Adult dispersal over large distances is probably caused by strong wave action during storms or when it anchors itself to floating debris (Ref. 52034).
Is thought to live for 3-5 years (Ref. 52034). Because of its short generation time and multiple breeding cycles during each spawning season, resilience is thought to be high. However, in tropical areas where seagrass beds are regularly exploited for other species of seahorses for the aquarium trade, traditional medicine, etc., populations have been quickly eradicated (Ref. 89253). Feeds on small prey and organic debris. Has been reared in captivity (Ref. 35416).
Ovoviviparous, with the female depositing eggs into the male brood pouch. During the mating season, mature males and females have been observed to change hue, i.e., become brighter, when greeting, courting, or mating (Ref. 88171). Newly hatched young are thought to have a planktonic stage that lasts at least eight weeks (Refs. 47822, 52034).
Lourie, S.A., A.C.J. Vincent and H.J. Hall, 1999. Seahorses: an identification guide to the world's species and their conservation. Project Seahorse, London. 214 p. (Ref. 30915)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; aquarium: show aquarium
More information
ReferencesAquacultureAquaculture profileStrainsGeneticsAllele frequenciesHeritabilityDiseasesProcessingMass conversion
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources